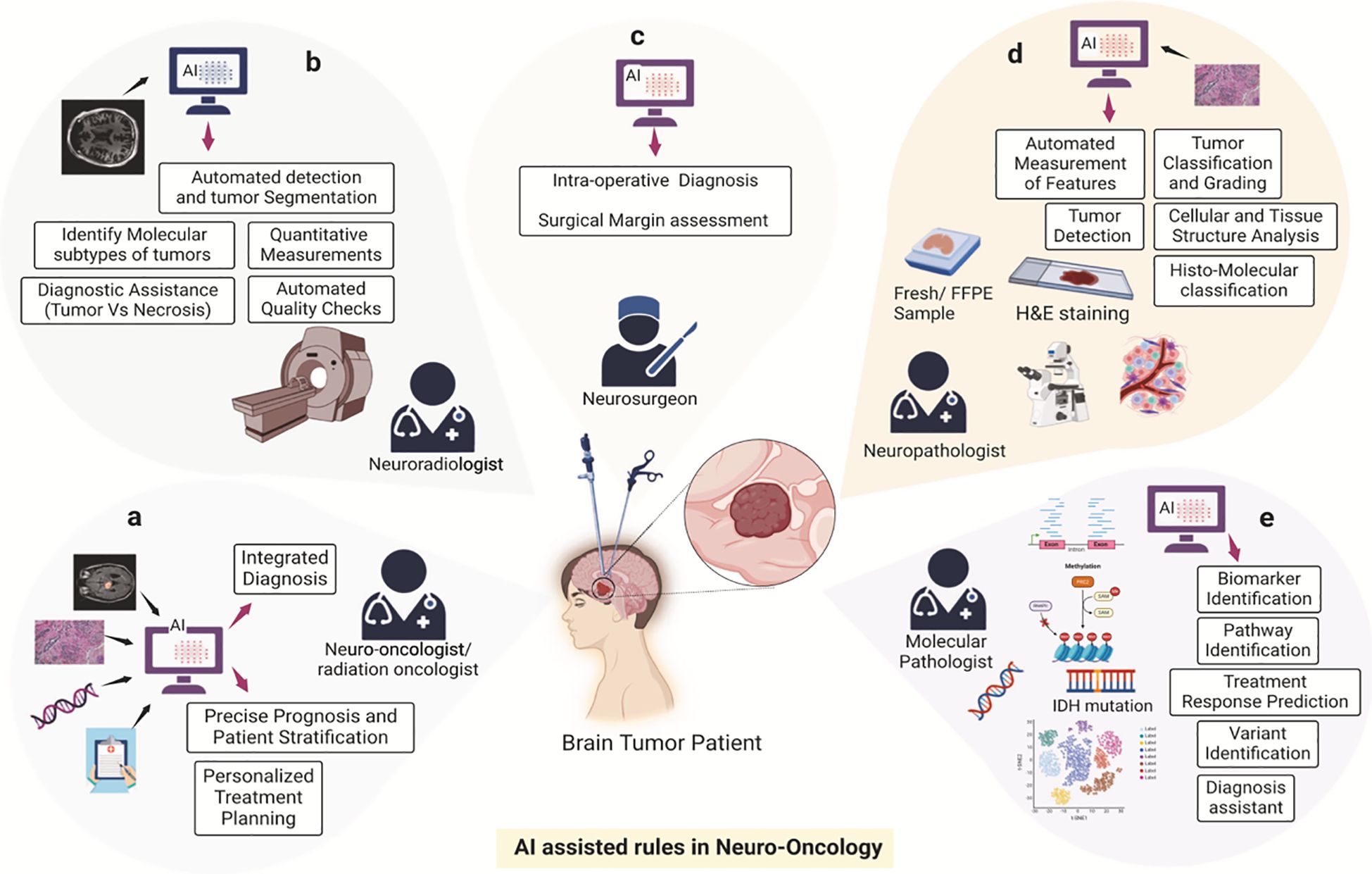
Oncology is a vital and rapidly evolving medical field focused on the study, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of cancer. In 2025, with advancements in genomics, immunotherapy, and personalized medicine, oncology is playing a more significant role than ever in saving lives and transforming patient care.
🧬 What Causes Cancer? A Genetic Perspective
Cancer is fundamentally a genetic disease. It occurs when mutations affect genes that regulate cell growth, division, and death. These mutations can be inherited or acquired due to environmental exposures (like smoking, UV radiation, or certain viruses). The result? Uncontrolled cell proliferation that may invade nearby tissues or spread to distant organs—what we call metastasis.

🧪 How Is Cancer Diagnosed?
In oncology, early detection is key. Today’s diagnostic methods go far beyond traditional biopsies. Here are some of the most common and advanced tools:
- Imaging techniques (MRI, CT scans, PET scans)
- Tumor marker tests
- Liquid biopsy – detecting cancer DNA in blood
- Next-generation sequencing (NGS) – identifying genetic mutations in tumors
Molecular diagnostics and AI-based imaging are now being used to detect tumors at earlier stages, when treatment is more effective.

💊 Oncology Treatment Options: From Chemotherapy to CAR-T Cells
Treatment strategies in oncology vary depending on cancer type, stage, and genetic profile. Standard treatments include:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy – drugs that attack specific cancer mutations
- Immunotherapy – harnessing the body’s immune system to fight cancer
- Cancer vaccines
- CAR-T cell therapy – genetically engineered immune cells
Modern oncology embraces a personalized medicine approach, meaning treatment is tailored to the patient’s unique genetic and molecular tumor profile.
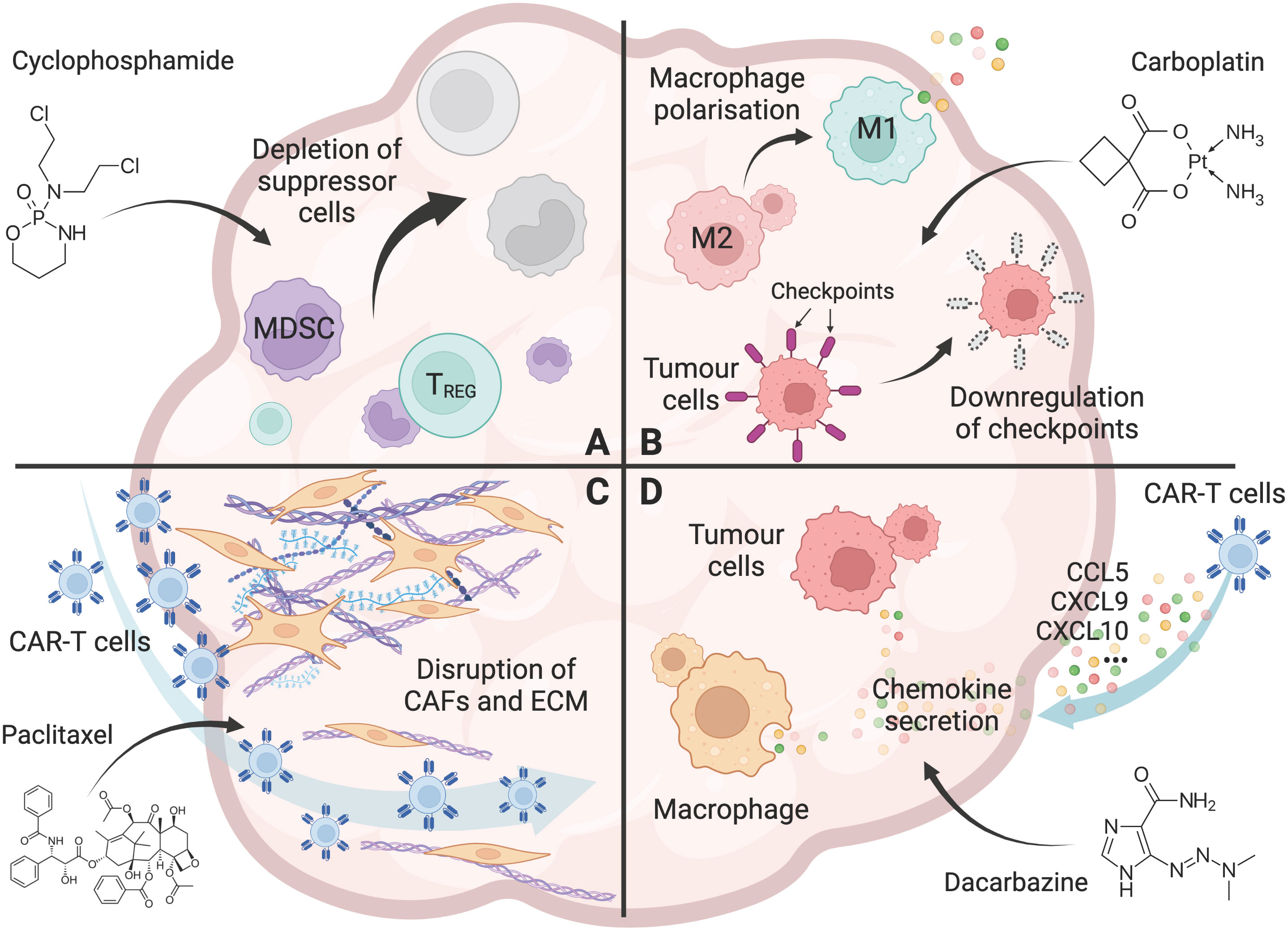
🧠 Why Is Oncology Research So Important?
Cancer remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, but oncology research is unlocking new hope. Clinical trials are testing innovative therapies, including:
- Checkpoint inhibitors to reactivate immune cells
- mRNA-based vaccines (similar to COVID-19 vaccines)
- Biomarker-driven therapy for targeted results
- Organoid models to test drugs on patient-derived mini-tumors
This continuous progress is turning certain cancers from fatal diseases into chronic, manageable conditions.
🧑⚕️ The Role of Oncologists and Multidisciplinary Care
An oncologist is a physician who specializes in cancer treatment. They often work with a team that includes:
- Radiologists
- Pathologists
- Surgeons
- Genetic counselors
- Nurses and support staff
This multidisciplinary approach ensures the best outcomes by combining expertise in diagnostics, treatment, nutrition, and psychological support.

🌍 The Future of Oncology: AI, Genomics & Accessibility
Looking ahead, oncology is becoming more precise, accessible, and data-driven. Key trends shaping the future include:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) for image analysis and treatment planning
- earable biosensors for real-time monitoring
- Telemedicine for remote consultations
- Global cancer screening programs in underserved regions
- CRISPR gene editing to correct cancer-causing mutations
- CRISPR gene editing to correct cancer-causing mutations